说明
ConcurrentHashMap并发容器
- 采用 cas自旋、while/for死循环、sychronize锁三种方式保证线程竞争下的插入安全,其原理与HashMap并不相同,改动量比较大
- jdk7采用分段segament的概念,把数组分为几段,每次锁一段达到并发的目的,但是分段会多维护一次hash
- jdk8采用锁数组的节点Node,将链表或红黑树整个锁定,达到线程安全。jdk8的精髓就在于没有node节点的时候数据的并发插入,它并没有阻塞线程,而是cas重试
源码解析
Jdk8源码
putValue()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
| final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K, V>[] tab = table; ; ) {
Node<K, V> f;
int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) {
tab = initTable();
} else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break;
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K, V> e = f; ; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K, V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K, V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K, V>) f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value))
!= null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
|
initTable()
核心就是循环判断tab容量
判断是否有其他线程已经开始了,有则放弃时间片进入下一次循环
没有则通过原子类获取执行权并设置sc为-1
初始化数组,初始化阈值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield();
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
|
helpTransfer()
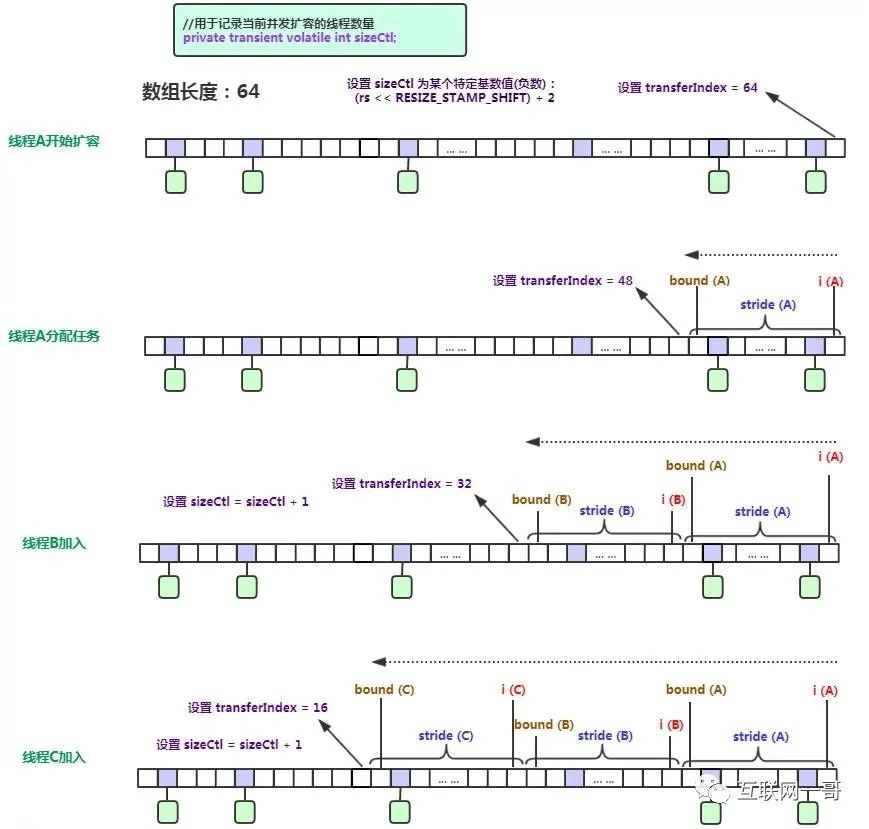
- 根据 CPU 核心数确定每个线程负责的桶数,默认每个线程16个桶
- 创建新数组,长度是原来数组的两倍
- 分配好当前线程负责的桶区域 [bound, nextIndex)
- 并发迁移,根据链表和红黑树执行不同迁移策略
- 迁移完成,设置新的数组和新的扩容阈值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
transfer(tab, nextTab);
break;
}
}
return nextTab;
}
return table;
}
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE;
if (nextTab == null) {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
|
扩容图文
多线程开始扩容{}
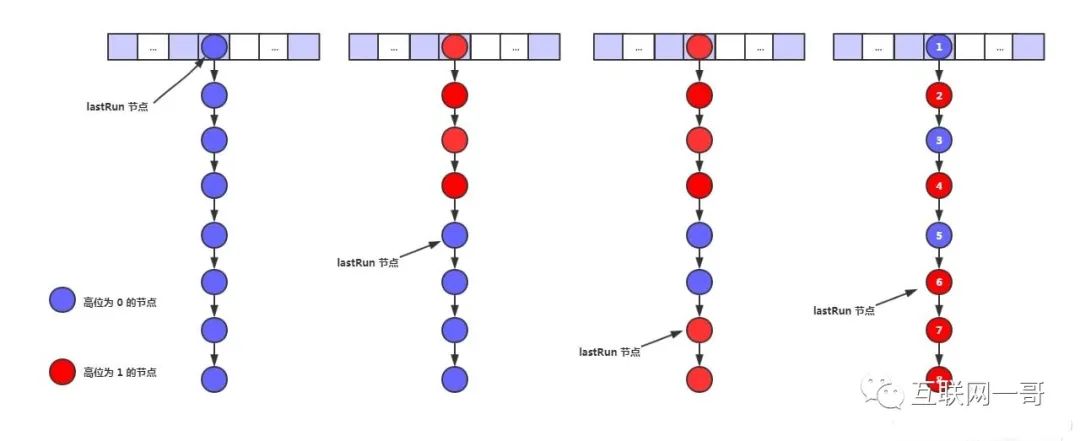
lastrun节点{}
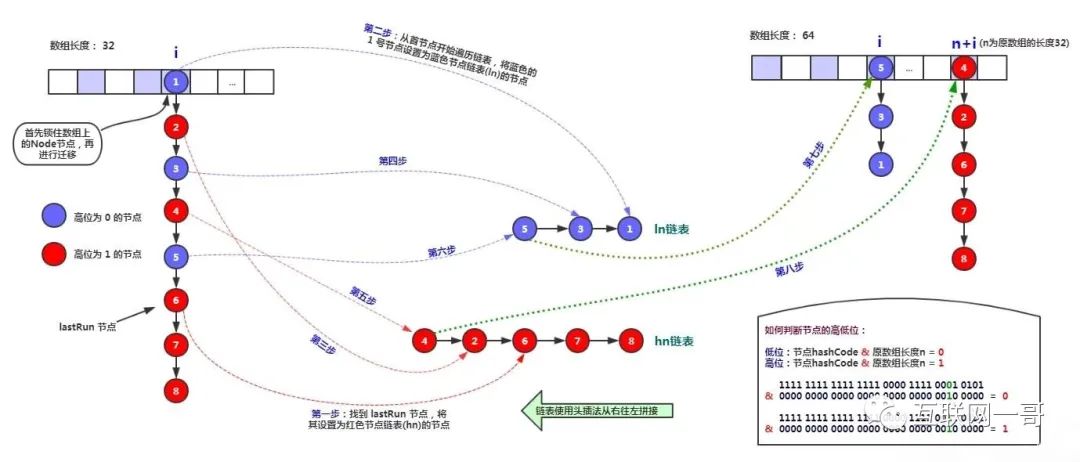
链表迁移{}
红黑树迁移{}
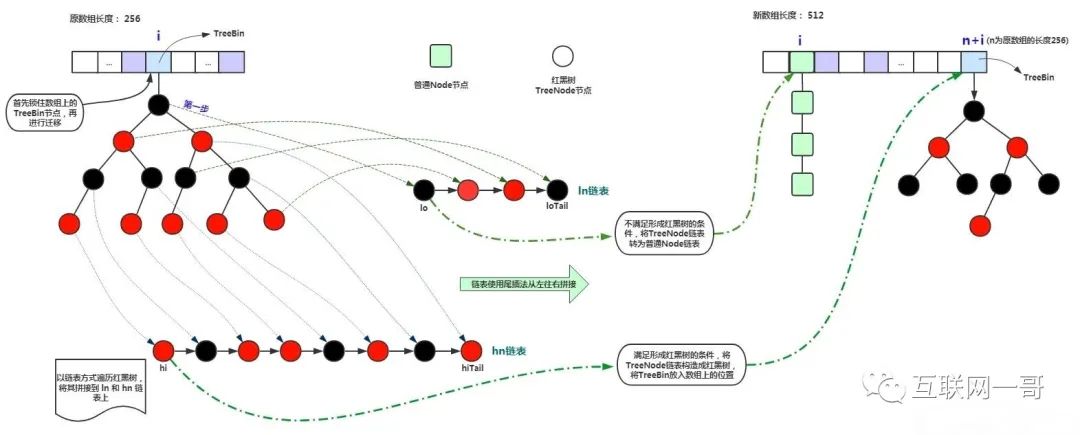
迁移过程中get和put的操作的处理{}
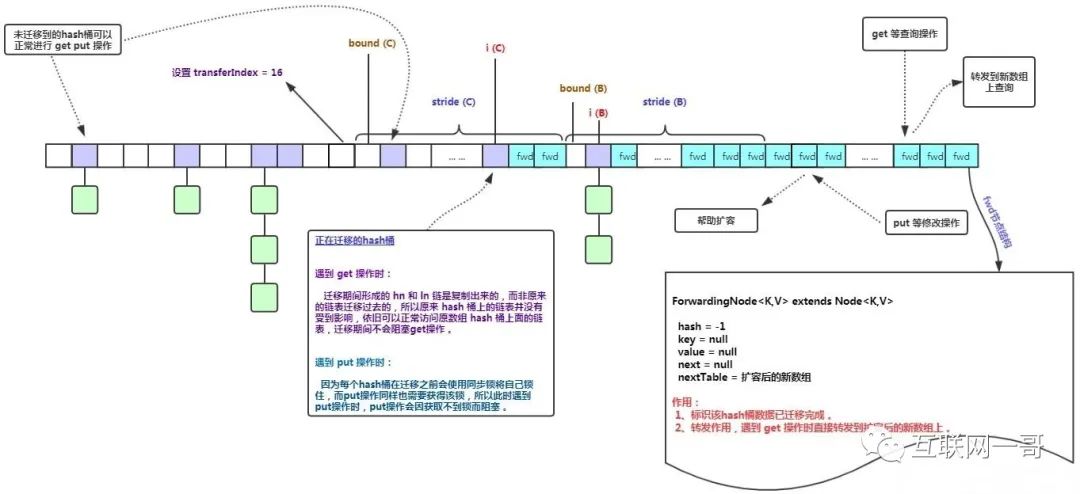
并发迁移{}
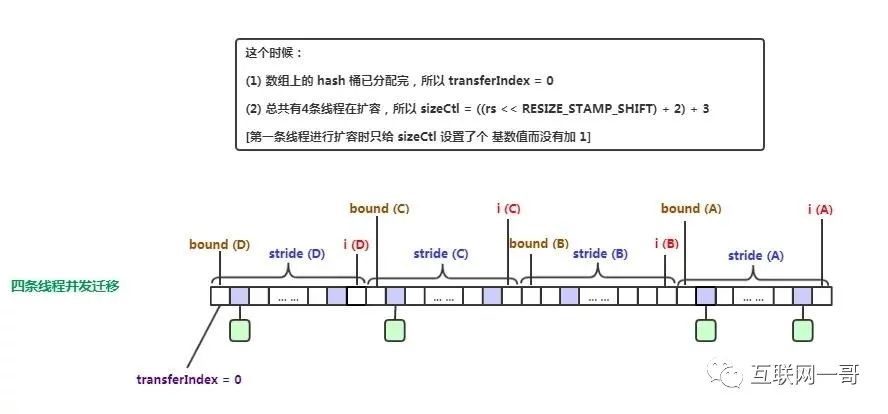
迁移完成{}
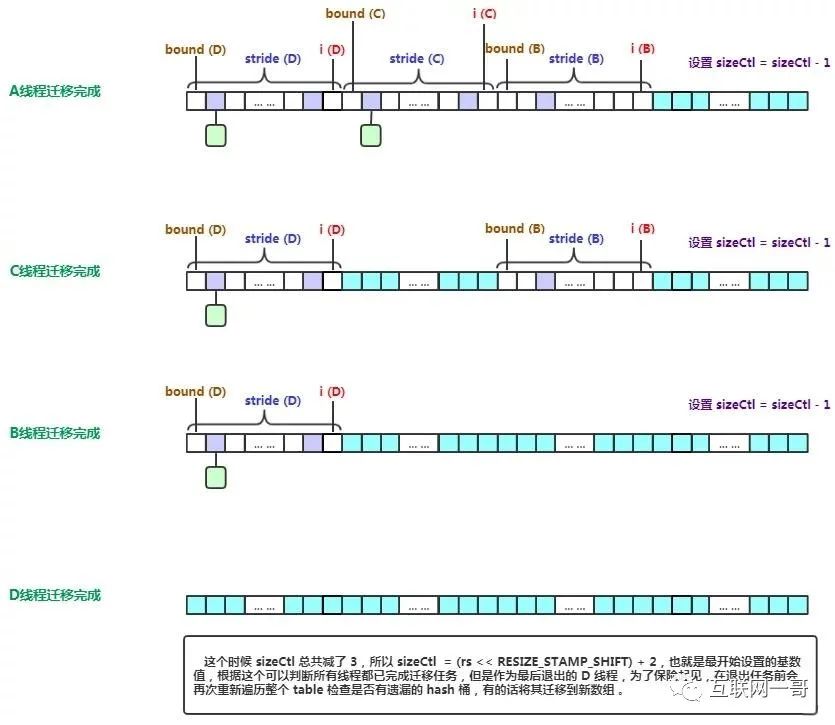
emm 引用至哪里,有点忘了,抱歉